A gyroscope is a device used to measure angular velocity, and based on its acceleration function, it can be further developed to construct a gyroscope.
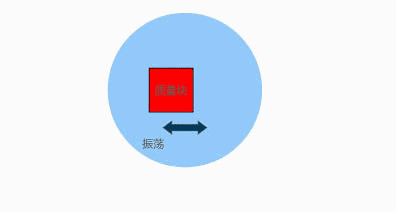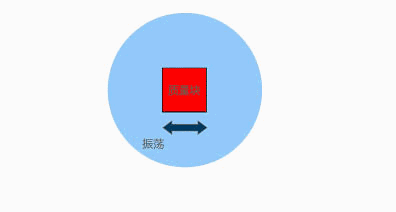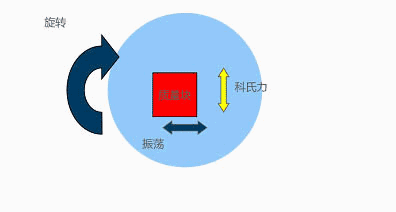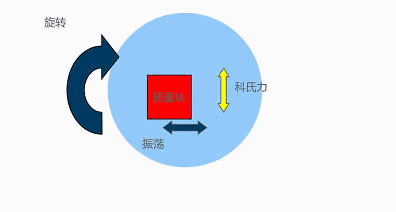
The internal principle of a gyroscope is as follows: a voltage is applied to a fixed finger and the voltage is alternately changed, causing a mass block to oscillate back and forth. When it rotates, Coriolis acceleration is generated, and it can be measured at this time; This is somewhat similar to an accelerometer, and the decoding method is roughly the same, both using amplifiers.

The angular velocity is determined by the measurement results of Coriolis acceleration
-Coriolis acceleration=2 × (w × mass velocity)
-W is the applied angular velocity (w=2 π f)
Fast coupling of velocity (periodic motion) applied through a 14 kHz resonant structure to the accelerometer frame
-The Coriolis acceleration has the same frequency and phase as the resonator, so it can counteract low-speed external vibrations
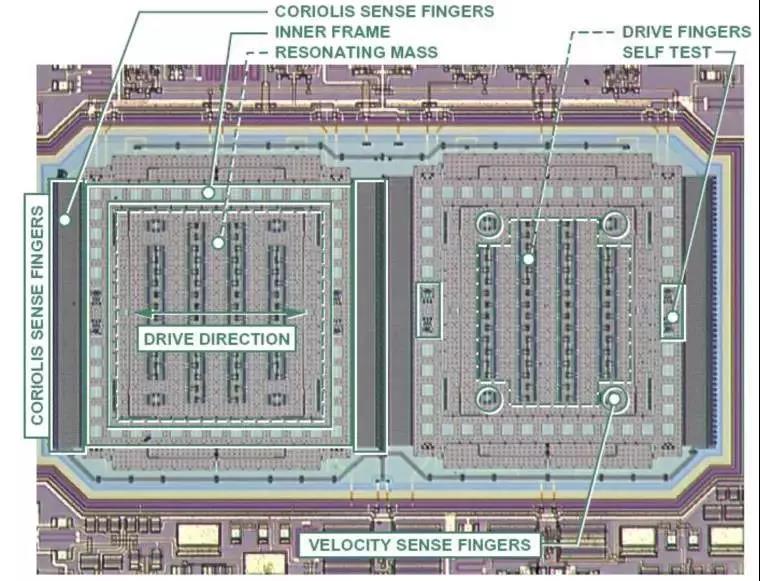
The structure of this mechanical system is similar to that of an accelerometer (micro machined polycrystalline silicon)
Signal conditioning (voltage conversion offset) uses technology similar to accelerometers
Apply a varying voltage to move the device back and forth, causing only horizontal movement without vertical movement. If rotation is applied, it can be seen that the device will move up and down, and the external finger will perceive the motion, thus being able to pick up signals related to rotation.
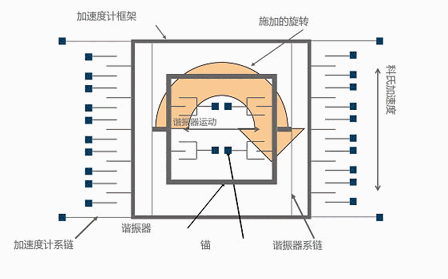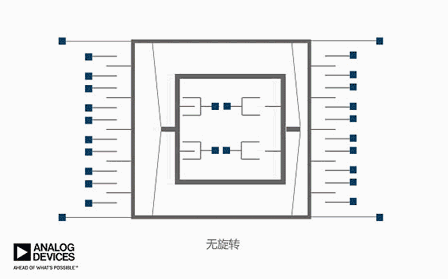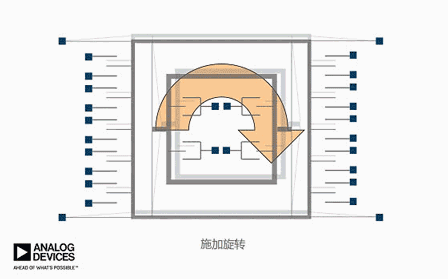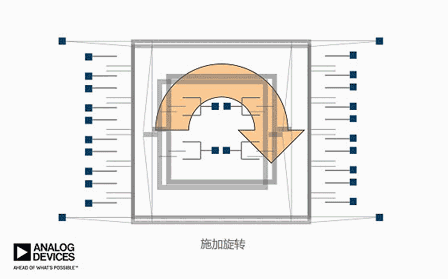
The animation above only abstractly demonstrates the working principle of a gyroscope, while the actual internal structure of a gyroscope looks like this. Don't accidentally misunderstand~
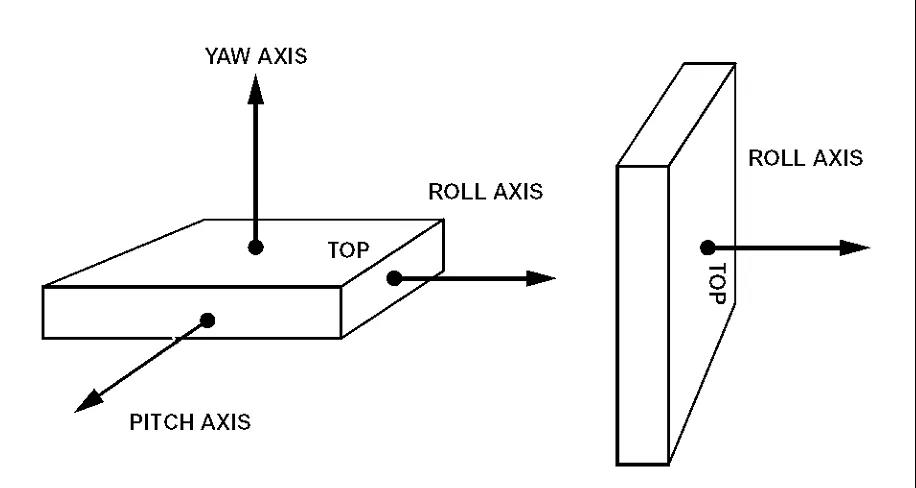
PS: Gyroscopes can be designed together with three corresponding to the so-called roll, pitch, and yaw. Anyone familiar with aircraft knows that pitch refers to the up and down direction of the aircraft, yaw refers to the left and right direction, and roll refers to rolling to the left or right. To control any type of aircraft or missile correctly, it is necessary to know these three parameters, which requires the use of gyroscopes. They are also often used for car navigation, and when the car enters a tunnel and loses GPS signal, these devices will record your whereabouts.
During flight operations, the drone images obtained usually carry accompanying POS data. Thus, it can be more convenient to process images during processing. POS data mainly includes GPS data and IMU data, which are the external azimuth elements in oblique photogrammetry: latitude, longitude, elevation, heading angle (Phi), pitch angle (Omega), and roll angle (Kappa).
GPS data is generally represented by X, Y, and Z, representing the geographical location of the exposure point of the aircraft during flight.

Flight control is composed of a main control MCU and an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU). IMU provides raw data of the spacecraft's attitude in space, usually provided by gyroscope sensors/accelerometer sensors/electronic compass to obtain the spacecraft's 9DOF data.
The sensors in IMU are used to sense the attitude and motion status of the aircraft in the air, which is a proprietary term called motion sensing tracking. There are four main types of basic motion sensors in motion sensing technology, and the principles of motion sensing and tracking are explained below.
MEMS
The sensors used in IMU are mostly microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which are a very important branch of the semiconductor industry.
Micro Electro Mechanical System (MEMS) is an advanced manufacturing technology platform. Micro electromechanical systems are micrometer sized mechanical systems developed based on semiconductor manufacturing technology.
The acceleration gyroscope MPU6050 and electronic compass HMC5883L used on quadcopters are both microelectromechanical systems, belonging to the sensing MEMS branch. Sensing MEMS technology refers to devices and systems that are fabricated using microelectronics and micro mechanical processing, and use sensitive components such as capacitors, piezoelectrics, piezoresistives, thermocouples, resonances, tunneling currents, etc. to sense and convert electrical signals.
G-sensors
Accelerators can be used to sense linear acceleration and tilt angle, and single or multi axis accelerators can sense the amplitude and direction of combined linear and gravitational acceleration. Products with accelerators can provide limited motion sensing capabilities.
The accelerometer has good low-frequency characteristics and can measure low-speed static acceleration. On our aircraft, it is the measurement and analysis of the gravitational acceleration g (also known as the static acceleration mentioned earlier), and other instantaneous accelerations can be ignored. Remembering this is crucial for understanding the fusion of attitude calculation.
When we hold the accelerometer in our hand and rotate it freely, we see the component values of gravitational acceleration on three axes. When an accelerometer is in free fall, its output is 0. Why is this happening? This involves the design principle of an accelerometer: the accelerometer measures acceleration through specific force, not through acceleration.
Gyros
A gyroscope is an angular motion detection device that utilizes the momentum of a high-speed rotating body to sense the relative inertial space of the housing around one or two axes orthogonal to the rotational axis. The angular motion detection device, also known as a gyroscope, which uses other principles to perform the same function.
Gyroscopes can sense the rotational angular velocity of one or more axes and accurately sense complex movements in free space. Therefore, gyroscopes have become necessary motion sensors for tracking the direction and rotation of objects. Unlike accelerators and electronic compasses, gyroscopes do not require any external forces such as gravity or magnetic fields to autonomously perform their functions. So theoretically, it is possible to complete attitude navigation tasks using only a gyroscope.
The characteristic of a gyroscope is that it has good high-frequency characteristics and can measure high-speed rotational motion. The disadvantage is the existence of zero drift, which is easily affected by temperature/acceleration, etc.
E-Compasses
An electronic compass, also known as a digital compass or magnetometer, is a method of using the geomagnetic field to determine the North Pole. Nowadays, electronic compasses made of magneto resistive sensors and flux gates are commonly used.
An electronic compass can sense direction from the Earth's magnetic field. Consumer electronics applications that utilize electronic compasses, including displaying correct directions in mobile map applications or providing forward direction data for navigation applications. However, the magnetic field interference of electronic devices or building materials is stronger than that of the Earth's magnetic field, making the output value of electronic compass sensors more susceptible to various environmental factors, especially indoors. Therefore, electronic compasses require frequent calibration to maintain the accuracy of forward direction data.
Barometers
Pressure sensors, also known as barometers, sense the relative and absolute height of objects through changes in air pressure. They are often used in consumer products related to sports, fitness, direction estimation, and other applications. For example, they can sense the user's movement floor and adjust map information.
IMU data mainly includes three data points: heading angle (Phi), pitch angle (Omega), and roll angle (Kappa).
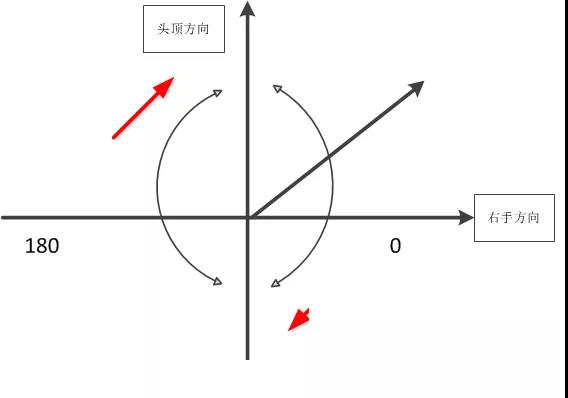
1. Phi
The abbreviation for heading angle in English is Phi. Defined as the angle between the longitudinal axis of an airplane or space shuttle and the North Pole of the Earth.
The schematic diagram is shown in the following figure:
2. Omega
The abbreviation for pitch angle in English is Omega. Defined as: the angle between the vector parallel to the fuselage axis and pointing towards the front of the aircraft and the ground.
The schematic diagram is as follows:
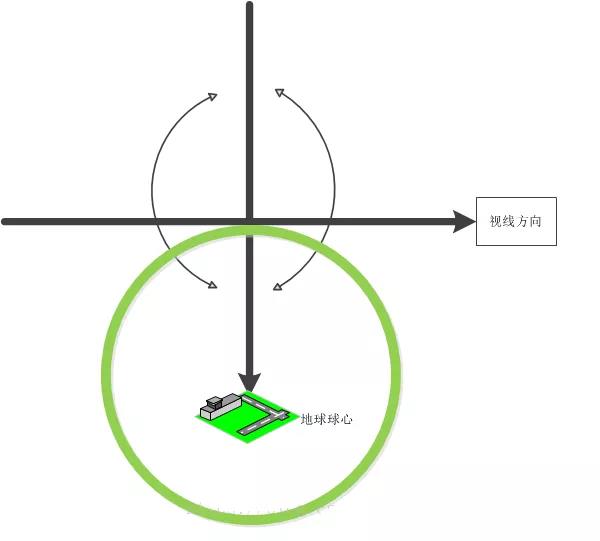
3. Kappa
Roll angle, also known as roll angle, abbreviated as Kappa in English. Defined as the angle between the optical axis and the tenth circle.
The schematic diagram is shown in the following figure:
Wuxi Huilian Information Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research, development, production, and sales of various types of fiber optic gyroscopes, MEMS gyroscopes, tilt sensors, inclinometers, leveling instruments, electronic compasses, GPS, Beidou navigation, as well as AHRS, IMU, and integrated navigation systems. Especially in the field of fiber optic gyroscopes, the company adopts a unique digital closed-loop solution and has multiple patented technologies, making it one of the competitive fiber optic gyroscope suppliers in China.
The multi-faceted cooperation with Peking University Regional Fiber Optic Communication Network and National Laboratory of New Optical Communication Systems has established the company's rich technical reserves and strong research and development capabilities, and created an inertial navigation service platform with independent intellectual property rights. The company currently has various precision products applied in multiple fields such as oil well inclinometer, inertial north finding, navigation, guidance, platform stability, attitude control, etc., and has the ability to develop customized products according to customer needs. Welcome to inquire by phone.
Note: Some of the image content is selected from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for deletion. Thank you!