Autonomous driving has become a definite trend in the development of the automotive industry, and its greatest significance lies in freeing the hands of drivers and bringing about the first seamless connection of human spatial significance.
The three core questions of autonomous driving are: Where? Where are we going? How to go?
Among them, the positioning system focuses on solving the problem of 'where is it?' in autonomous driving.
The three main positioning technologies for autonomous driving
There are usually three technical methods for obtaining positioning in autonomous driving:
1. Signal based positioning: Represented by the technology of positioning through satellite signals from global GNSS satellites, other technologies include obtaining information using signals such as WIFI, FM microwave, etc;
2. Environmental feature matching: Based on visual or LiDAR positioning, the observed features are matched with semantic or feature maps in the database to obtain the position and attitude of the vehicle;
3. Inertial positioning: A positioning technology that relies on inertial sensors to obtain acceleration and angular velocity information, and calculates the current position and orientation through calculation.
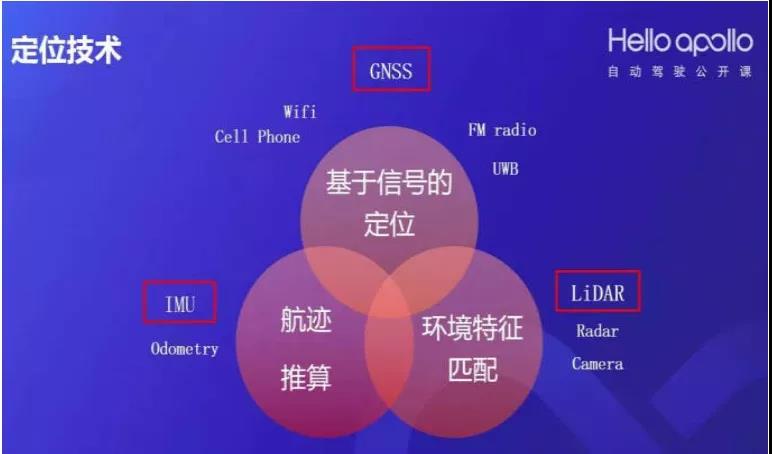
Baidu Apollo uses three positioning technologies
Source: Baidu Apollo, Evergreen Foundation
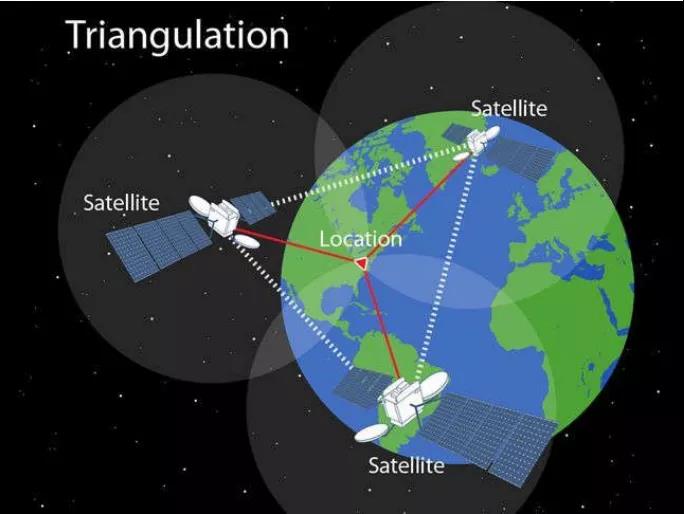
1. GNSS positioning
GNSS positioning technology is a mature and commonly used technology. GNSS uses triangulation to accurately locate any position on the Earth's surface using three or more satellites.
Principles of GNSS positioning technology
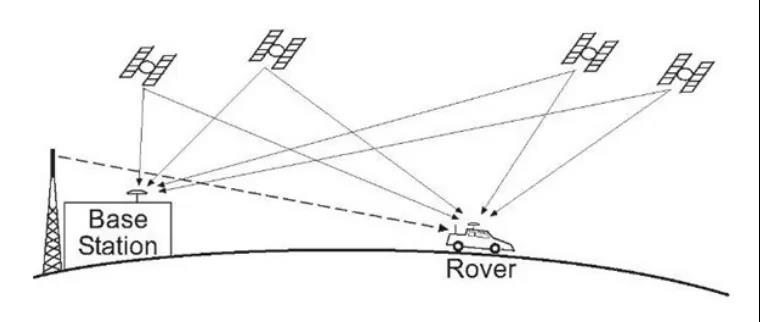
Autonomous driving typically uses real-time kinematic (RTK) technology to achieve high-precision positioning.
Firstly, a base station needs to be built on the ground. When establishing a base station, accurate location information such as latitude and longitude can be obtained.
When the distance between the GNSS receiver of the base station and the GNSS receiver of the vehicle is less than 30km, it can be considered that their GNSS signals pass through the same atmospheric area, that is, the signal errors of the two are basically the same.
Based on the precise location of the base station and the time of signal propagation, the signal propagation error at this time can be inferred, and then the GNSS signal of the vehicle can be corrected using this error to reduce the impact of cloud cover, weather, and other factors on signal transmission, thereby achieving high-precision (decimeter or even centimeter level) positioning.
The positioning accuracy of GNSS-RTK technology is high and stable, and it has been widely used in autonomous driving navigation systems. However, this method also has a significant drawback - it relies on satellite signals. At least three visible satellites are required for successful positioning. However, in actual operating environments such as urban canyons, due to multipath effects and satellite signal occlusion, the number of visible satellites may be insufficient, which will affect the accuracy and reliability of GNSS RTK positioning and velocity measurement.
2. Environmental feature matching and localization
By using sensors such as cameras and LiDAR, surrounding environmental information can be obtained, and after processing, location information can also be obtained.
Schematic diagram of environmental feature matching and localization
Taking laser positioning as an example, laser point cloud positioning generally first obtains real-time point clouds on the vehicle through laser radar, and obtains a massive set of points for the spatial distribution and surface characteristics of the target. The processed point cloud data is matched with a pre made map to obtain the distance, angle, and boundary information of the vehicle.

3. Inertial positioning
Obtain the acceleration and angular velocity at each moment from inertial sensors (including accelerometers and gyroscopes), integrate them over time to obtain velocity and angle, and then calculate the real-time position through spatial accumulation.
Schematic diagram of inertial positioning principle
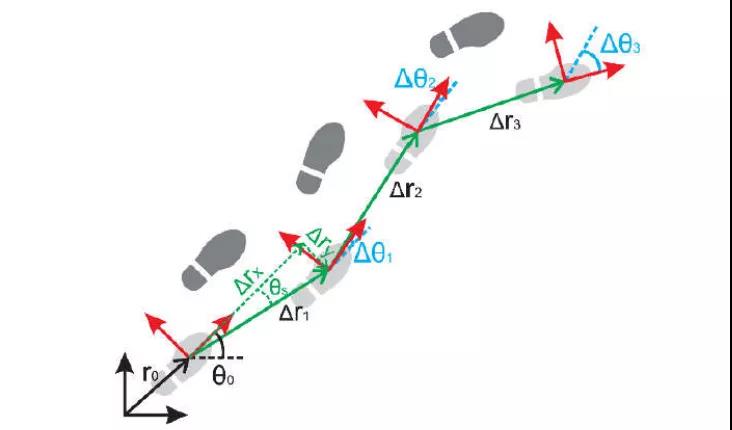
These three positioning methods each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Among them, inertial navigation positioning can ensure that it is not affected by external information, and output vehicle motion parameters at high frequencies at any time, providing continuous vehicle position and attitude information for the decision-making center, which has advantages that no sensor can match. Inertial navigation system is an essential key component in high-precision positioning.
The core keyword of autonomous driving positioning system is high precision. High precision positioning can realize lane level positioning in extreme weather and environment. High precision positioning should be able to achieve spatio-temporal synchronization of perception information, reduce the computing power requirements of the auto drive system, reduce the complexity of the system, and be conducive to the realization of V2X applications and the safety and comfort of automatic driving.

Inertial navigation system is an essential key component in autonomous driving
Inertial navigation is irreplaceable in autonomous driving positioning systems. Inertial navigation has unique advantages such as uninterrupted output information and immunity to external interference, which can ensure the high-frequency output of vehicle motion parameters at any time, providing continuous vehicle position and attitude information for the decision-making center, which is incomparable to any sensor.
Inertial navigation system is the only device that can output complete six degrees of freedom data. Inertial navigation can calculate the translation (position, velocity, acceleration) and rotation (angle, angular velocity) of x, y, and z dimensions, and can infer the measured values of other sensor states through observation models. The difference between predicted and measured values is used for weighted filtering. Inertial navigation is the only option for obtaining real-time attitude, azimuth, velocity, and position.
Inertial navigation has a higher frequency of data updates and can provide high-frequency positioning results output. The frame rate of the camera is generally 30Hz, with a time uncertainty of 33ms; GNSS delay is generally 100-200ms; The delay in predicting the state of inertial navigation is as short as a few milliseconds, so inertial navigation can be used to estimate and compensate for the delay of other sensors, achieving global synchronization.
When the vehicle is driving, the delay of GNSS is 100ms. When the camera captures environmental targets, the actual position of the image will be inconsistent with the position reported by GNSS. Assuming that the car is traveling at a speed of 120km/h, a delay of 100ms means a delay of 3.3 meters. At this time, the accuracy of map and target recognition becomes meaningless no matter how high it is. If combined inertial navigation is used, the delay in position will be about 2.5ms, resulting in an error of only 0.08m, which can better ensure the safety of driving.
Inertial navigation is the fusion center of positioning information, integrating information from LiDAR, cameras, and vehicle systems. In L3 and higher level autonomous vehicle, more sensors will be introduced to support the functions of the system. Inertial navigation system is the main body of all positioning technologies that is most easy to realize the fusion with the positioning information provided by other sensors. As the center of positioning information fusion, it will further fuse the information of visual sensors, radar, laser radar and body system to provide accurate, reliable and continuous vehicle position and attitude information for the decision-making level.
Wuxi Huilian Information Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise dedicated to the research, development, production, and sales of various types of fiber optic gyroscopes, MEMS gyroscopes, tilt sensors, inclinometers, leveling instruments, electronic compasses, GPS, Beidou navigation, as well as AHRS, IMU, and integrated navigation systems. Especially in the field of fiber optic gyroscopes, the company adopts a unique digital closed-loop solution and has multiple patented technologies, making it one of the competitive fiber optic gyroscope suppliers in China.
The multi-faceted cooperation with Peking University Regional Fiber Optic Communication Network and National Laboratory of New Optical Communication Systems has established the company's rich technical reserves and strong research and development capabilities, and created an inertial navigation service platform with independent intellectual property rights. The company currently has various precision products applied in multiple fields such as oil well inclinometer, inertial north finding, navigation, guidance, platform stability, attitude control, etc., and has the ability to develop customized products according to customer needs. Welcome to inquire by phone.
Note: Some of the image content is selected from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for deletion. Thank you!
(Editor: Huilian Technology)